[JS-Basics] Basics
JavaScript 共有八种数据类型,分别是 Undefined、Null、Boolean、Number、String、Object、Symbol、BigInt。
这些数据可以分为原始数据类型(primitives)和引用数据类型(Object):
- 栈(stack):原始数据类型(string, number, bigint, boolean, symbol, null and undefined)
- 堆(heap):引用数据类型(对象 object、数组 array 和函数 function)
两种类型的区别在于存储位置的不同:
- 原始数据类型直接存储在栈(stack)中的简单数据段,占据空间小、大小固定,属于被频繁使用数据,所以放入栈中存储; (primitive types => by value)
- 引用数据类型存储在堆(heap)中的对象,占据空间大、大小不固定。如果存储在栈中,将会影响程序运行的性能;引用数据类型在栈(stack)中存储了指针,该指针指向堆中该实体的起始地址。当解释器寻找引用值时,会首先检索其在栈中的地址,取得地址后从堆中获得实体。(object => by reference)
Primitives
(string, number, bigint, boolean, symbol, null and undefined)
Object
(function, array(ordered collections), objects(keyed collections), Map(like object, but allows key to be any type), Set(collection of unique values))
- Object.keys, values, entries are common agreement to use for data structure, ex,Map,Set,Array,Object
- Object's filter,map... method
- Map & Set
- weakMap
for...of vs for...in
The for...in loop logs only enumerable properties(indexes) of the iterable object
- 常被用在 object 中來得到 object 的 key
- for-in 缺點 =>
//key值為Symbol時會自動忽略
const obj = { a: 1 };
const sym = Symbol("b");
obj[sym] = 2;
for (const prop in obj) {
console.log(prop); // "a"
}
//只會loop through enumerable,透過defineProperty可以設定object得flag/attributes
const obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };
Object.defineProperty(obj, "c", { value: 3, enumerable: false });
for (const prop in obj) {
console.log(prop); // "a", "b"
}
- The for...of loop iterates and logs values that iterable, as an array (which is iterable), defines to be iterated over.
- 常被用在 array, Map, Set, user-defined iterable(generator)...
Object.prototype.objCustom = function () {};
Array.prototype.arrCustom = function () {};
const iterable = [3, 5, 7];
iterable.foo = "hello";
for (const i in iterable) {
console.log(i);
}
// "0", "1", "2", "foo", "arrCustom", "objCustom"
for (const i in iterable) {
if (Object.hasOwn(iterable, i)) {
console.log(i);
}
}
// "0" "1" "2" "foo"
for (const i of iterable) {
console.log(i);
}
// 3 5 7
Set
const mySet = new Set();
mySet.add(1);
mySet.has(5)
mySet.size
mySet.delete(5)
mySet.clear()
//Array to Set
var arr = [55, 44, 65];
var set = new Set(arr);
//set to Array
1. const array = Array.from(mySet);
2. const array = [...mySet];
Map
// 建立 Map 時直接代入內容
let myMap = new Map([
[1, "a"],
[2, "b"],
]);
map.set(key, value);
map.has(key); //boolean
map.size();
map.get(key); //value
map.delete(key);
map.clear();
//convert Object to Map
const map1 = new Map(Object.entries(obj));
//convert Map to Object
const objAgain = Object.fromEntries(map1);
//convert map keys to an array
const mapKeys = Array.from(map.keys());
//convert map keys to an object
const mapKeys = Array.from(map.values());
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20069828/how-to-convert-set-to-array
weakMap vs Map & weakSet vs Set 的差別
- WeakMap 只接受 object 當作 key ; WeakSet 只接受 object 為裡面的值
- references to key objects are held "weakly", which means that they do not prevent garbage collection in case there would be no other reference to the object. 代表如果沒有其他地方有引用 weakMap 中的 key 的話,key 和 WeakMap 就會被 GC。
object vs Map 的差別
- object 中的 key 只能是 string 或是 symbol,Map 中的 key 則可以是任何值
- 原始物件的元素沒有順序性,Map 物件則有順序,所以在 Leetcode 時 Map 會比較好用
- Map 提供其他的 method,object 則沒有。ex, Map.size(), Map.clear()
- Map 可以直接迭代,利用
for..of或是forEach等方法, object 則只能用for...in來取得 key 值或是利用Object.entries跟Object.keys來迭代
Object 中的自動排序機制
範例:
let object = {};
object[3] = "3";
object[1] = "1";
// {1: '1', 3: '3'}
總結:
如果 key 是數字的情況,數字先的會被排在前面。string 則是沒有這樣的問題。
https://juejin.cn/post/7105216353564360711 https://www.explainthis.io/zh-hant/interview-guides/javascript/map-vs-object
Property flags and descriptors
[define]https://javascript.info/property-descriptors
透過 Object.defineProperty的語法來更改 object 該 key-value pair 的設定。
let user = {
name: "John",
};
Object.defineProperty(user, "name", {
writable: false,
});
user.name = "Pete"; // Error: Cannot assign to read only property 'name'
透過Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor可以來查看目前該 property 的設定。
let user = {
name: "John",
};
let descriptor = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(user, "name");
console.log(descriptor);
// {
// "value": "John",
// "writable": true,
// "enumerable": true,
// "configurable": true
// }
Heap and Stack
Stack(Static memory allocation)
- A stack is a data structure that JavaScript uses to store static data. Static data is data where the engine knows the size at compile time. In JavaScript, this includes primitive values (strings, numbers, booleans, undefined, and null) and references, which point to objects and functions.
- primitive values
- references, which point to objects and functions
The stack contains a reference to the object in the heap: The memory of the heap is not ordered in any particular way, which is why we need to keep a reference to it in the stack.
Since the engine knows that the size won't change, it will allocate a fixed amount of memory for each value. The process of allocating memory right before execution is known as static memory allocation. Because the engine allocates a fixed amount of memory for these values, there is a limit to how large primitive values can be.
Heap(Dynamic memory allocation)
- The heap is a different space for storing data where JavaScript stores objects and functions and it allocate a fixed amount of memory for these objects. Instead, more space will be allocated as needed.
Type coercion 強制轉型
+:會轉成 string
-:會被轉為 number,如果不行轉成數字的話結果會是 NaN
null vs undefined
undefined is used to describe variables that do not point to a reference.
null is used to define something programmatically empty.
TLDR; Don't use the undefined primitive. It's a value that the JS compiler will automatically set for you when you declare variables without assignment or if you try to access properties of objects for which there is no reference. On the other hand, use null if and only if you intentionally want a variable to have "no value".
type null vs undefined
:當比較 null 和 undefined 的值的時候,使用非嚴格相等(==)會相同,所以必須使用 typeof 或是嚴格相等(===)。
constructor function vs function
語法:常規函數使用 function 關鍵字定義,後面是函數名稱和參數列表(如果有的話)。構造函數也是類似的方式定義,但通常使用大寫字母命名以表示應該使用 new 關鍵字調用它。
返回值:常規函數可以返回任何值,包括 undefined。另一方面,當使用 new 關鍵字調用構造函數時,它隱式地返回一個基於其原型的新對象。
用法:常規函數可以直接調用或賦值給變量,而構造函數通常使用 new 關鍵字調用以創建對象的新實例。
屬性和方法:常規函數可以具有自己的屬性和方法,但這些不會被創建函數的對象共享。另一方面,構造函數可以在其原型上定義屬性和方法,這些屬性和方法將被所有使用該函數創建的對象繼承。
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
let john = new Person("John", 30); // 創建一個新的 Person 對象
console.log(john.name); // 輸出 "John"
console.log(john.age); // 輸出 30
在普通 function 中的 this 會指向 windows
arrow function vs function
arrow function pros:
- readability
arrow function cons:
- this 指向上一層
- Do not have arguments
- Can’t be called with new
- They also don’t have super.
不該使用的時機: 需要使用 this 的時候,因為會指向上一層(很多時候是 window)
ex.Array.prototype.forEach = () => {
this; // 指向window,而不是Array
};
為什麼 arrow function 不能使用new?
因為 arrow function 不是 constructor 也沒有[[Construct]]這個方法,所以沒有辦法使用 new,也沒有 this。
Follow up
實現一個功能讓構造函數只能 new 操作,否則報錯
function Person(firstName, lastName) {
// this instanceof Person
// 如果返回值為 false,說明為普通調用
// 返回類型錯誤信息——當前構造函數需要使用 new 調用
if (!(this instanceof Person)) {
throw new TypeError(
'Function function Object() { [native code] } A cannot be invoked without "new"'
);
}
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.fullName = this.firstName + this.lastName;
}
// 當作普通函數調用
// Uncaught TypeError: Function function Object() { [native code] } A cannot be invoked without "new"
console.log(Person("戰場", "小包"));
call, apply and bind
:call, apply 會立即把 this 綁定在 call/apply 的第一個值,讓函式可以動態使用 this。 :bind 會建立新的函式,在被呼叫之後才會綁定。
fun.call(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, ...]]])
:設定 thisArg 值,並且把該 this 綁定在 thisArg 上,後面的參數為原先 function 的 argument.
var person = {
fullName: function () {
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;
},
};
var person1 = {
firstName: "Bill",
lastName: "Gates",
};
var person2 = {
firstName: "Steve",
lastName: "Jobs",
};
person.fullName.call(person1); // 将返回 "Bill Gates"
var person = {
fullName: function (city, country) {
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName + "," + city + "," + country;
},
};
var person1 = {
firstName: "Bill",
lastName: "Gates",
};
person.fullName.call(person1, "Seattle", "USA"); //Bill Gates,Seattle,USA
call 實作
Function.prototype.myCall = function (target, ...args) {
target = target || window;
const symbolKey = Symbol();
target[symbolKey] = this;
const res = target[symbolKey](...args); // args本身是rest參數,搭配的變量是一個數組,數組解構後就可以一個個傳入函數中
delete target[symbolKey];
return res;
};
fun.apply(thisArg, [argsArray])
:用法和 call 類似,但是第二個 parameter 是 array
var person = {
fullName: function (city, country) {
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName + "," + city + "," + country;
},
};
var person1 = {
firstName: "Bill",
lastName: "Gates",
};
person.fullName.apply(person1, ["Oslo", "Norway"]); //'Bill Gates,Oslo,Norway'
apply 實作
Function.prototype.myCall = function (target, args) {
target = target || window;
const symbolKey = Symbol();
target[symbolKey] = this;
const res = target[symbolKey](...args); // args本身是rest參數,搭配的變量是一個數組,數組解構後就可以一個個傳入函數中
delete target[symbolKey];
return res;
};
fun.bind(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, ...]]])
:會建立新的函式,當函式被呼叫時,會將 this 關鍵字設為給定的參數。
const person = {
firstName:"John",
lastName: "Doe",
display: function () {
let x = document.getElementById("demo");
x.innerHTML = this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;
}
}
//沒有bind Person的話,在setTimeout後,display的this遺失,輸出結果會是undefined
let display = person.display.bind(person);
setTimeout(display, 3000);
//John Doe
https://www.w3schools.com/js/js_function_bind.asp
Event delegation 事件委派 & addEventListener
事件委託是將事件監聽器添加到父元素,而不是每個子元素單獨設置事件監聽器。當觸發子元素時,事件會冒泡到父元素,監聽器就會觸發,往下傳遞的過程被稱為捕捉(capturing),往上傳遞的過程被稱為冒泡(bubbling)
Event delegation 優缺點:
- event handler 可以大幅減少,只需要設定在父層
<ul onclick="alert(event.type + '!')">
<li>One</li>
<li>Two</li>
<li>Three</li>
</ul>
//當按到 <li> 其中任何一個onclick都會在bubbling時被觸發
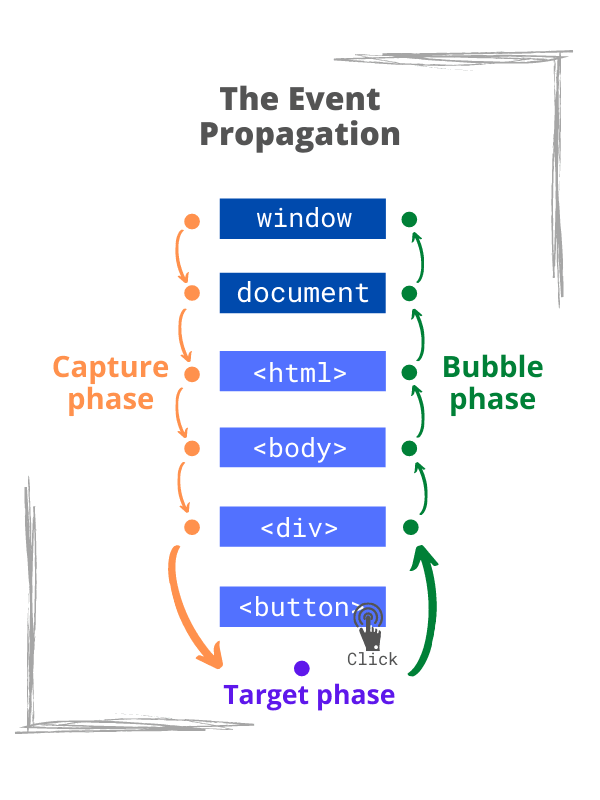
為什麼需要 Event delegation?
e.stopPropagation vs preventDefault
e.stopPropagation: 停止接下來的 bubbling 或是 capturing
preventDefault: 停止 browser 的預定行為(default action)ex,用 preventDefault 來阻止\跳轉頁面
addEventListener:document.addEventListener(event, function, Capture)
第三個 parameter,default 為 false,執行在冒泡階段,
設定為 true 時,執行在捕捉階段。
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1687296/what-is-dom-event-delegation
Strict Mode 嚴格模式
用法:在檔案前面加上 ’use strict'
在嚴格模式下,以下幾種狀況是不被允許的:
- 直接定義未宣告變數
- 使用 delete 刪除變數或函式
- 重複變數
- 跟其他很多狀況
this 指向
:this 是一個 keyword 指向一個 object,在不同情況下,根據 this 被執行的環境,會有不同的 this。 :this 指向(reference)object.而它的值不一定,會根據它被執行的地方(call site)所決定的,以下有四個 this 的規則:
- 如果執行 function 時,是用
new來執行的,那 this 會指向新建立的 object. - 如果執行 function 時,是用 call,apply,bind,那 this 會指向傳進來的 argument.
- 如果執行時,是 object 中的一個 method,那 this 會指向 dot 的左邊(該 object).
- 如果 function 執行時沒有以上條件,this 就會是全局對象. 瀏覽器環境下 this 的值指向 window 對象,但是在嚴格模式下('use strict'),this 的值為 undefined。
- 如果相同的規則都出現的話,排名前的會先執行。
- 如果包住 this 的 function 是 arrow function 的話,不適用上面的規則,因為它本身沒有 this,所以 this 會等同於上一層的 this。
用途: ex. 實作 array map method
const personA = {
name: "AAA",
doing: function () {
console.log(this);
},
};
personA.doing();
// {name: 'AAA', doing: f}
//當是arrow function時
const personB = {
name: "AAA",
doing: () => console.log(this),
};
personB.doing();
// window
function makeUser() {
return {
name: "John",
ref: this,
};
}
let user = makeUser();
alert(user.ref.name); // undefined, 因為ref不是一個function
https://medium.com/codeburst/the-simple-rules-to-this-in-javascript-35d97f31bde3 https://javascript.info/object-methods#this-in-methods
Number js method caveat
- when finding NaN value, use findIndex
- don't use indexOf, because it's strict equal(===)
findIndex() / indexOf()
- strict comparison(===)
include()
- loose comparison(==)
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/5294413/find-index-of-nan-in-a-javascript-array
ES6
break vs continue vs return
return => jump out of a function
break => jump out of a loop
continue => jump over one iteration in the loop
== vs === vs Object.js()
== 會先轉變型別再去做比較 === 會比較型別跟其值
===的缺點是在比較 -0、+0、NaN時會出現問題,這時候可以用 Object.is 來解決
console.log(Object.is(+0, -0)); // false
console.log(Object.is(NaN, NaN)); // true
0.1 + 0.2 === 0.3 嘛?為什麼?
閱讀文章 計算機在計算的時候,會先把數字轉換成二進制再進行計算,因此 0.1 和 0.2 轉換成二進制的時候尾數會發生無限循環,然後進行加減乘除運算時,JS 引擎對二進制多餘的尾數進行截斷,所以造成精度丟失。
解決方法
- Math.js 資料庫
- parseFloat() + toFixed()方法
+parseFloat((0.1 + 0.2).toFixed(10)) === 0.3; // true
https://www.jianshu.com/p/574df3eb8c09
Resources
call, apply, bind 建議文章 https://juejin.cn/post/7128233572380442660
resources resources-ch https://www.w3schools.com/jsref/met_document_addeventlistener.asp https://stackoverflow.com/questions/5963669/whats-the-difference-between-event-stoppropagation-and-event-preventdefault https://medium.com/itsems-frontend/javascript-strict-mode-d0a3aa74458b https://medium.com/@sunnyhuang.sc/%E6%8A%80%E8%A1%93%E7%AD%86%E8%A8%98-javascript-%E4%BD%95%E8%AC%82%E5%BC%B7%E5%88%B6%E8%BD%89%E5%9E%8B-coercion-%E4%BB%A5%E5%8F%8A%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E4%BD%9C%E5%88%B0%E8%BD%89%E6%8F%9B%E5%9E%8B%E5%88%A5-d7e39e30083 https://stackoverflow.com/questions/37587834/why-can-i-not-use-new-with-an-arrow-function-in-javascript-es6