[JS] The Execution Context, Call-stack and Event Loop
解決的問題: JS 本身是 single threaded,代表一次只能有一個 function 被執行。
The Execution Context
當程式碼被執行時,會產生 Global Execution Context。然後 engine 進入 creation phase ,四件事情會發生:
- 建立 global 物件,在 browser 中被稱作
window,在 Node 中被稱作global - create
this並且與 global 物件 binding - 建立一個 memory heap 來儲存 variables 和 function references
memory heap 的文章 - 把 function declarations (function s()...)儲存在 memory heap 然後把裡面的 variable 賦予
undefined
完成後,engine 會進入下一個階段execution phase。
在這個階段,程式碼會被一條條的執行,
- variable 會被賦予值,
- function 則會被執行,並且在每個 function 被執行時,engine 都會 create 一個
Function Execution Context(類似上面的Global Execution Context),但是 global 物件會被指到arguments物件,裡面會儲存所有傳進 function 的值。
keyword: Global Execution Context, creation phase, execution phase
當出現多個 function,觸發多個 Function Execution Context時,engine 又要怎麼處理呢?
The Call-stack
: The call-stack 是一種資料結構(stack)用來追蹤和管理function execution。
實際情況:The call-stack 依照 Last In First Out 的規矩,當 engine call 到 function 時,會把該 function push 到 call-stack 裡,並且在執行該 function 時,會把該 function 從call-stack 中 pop 掉,
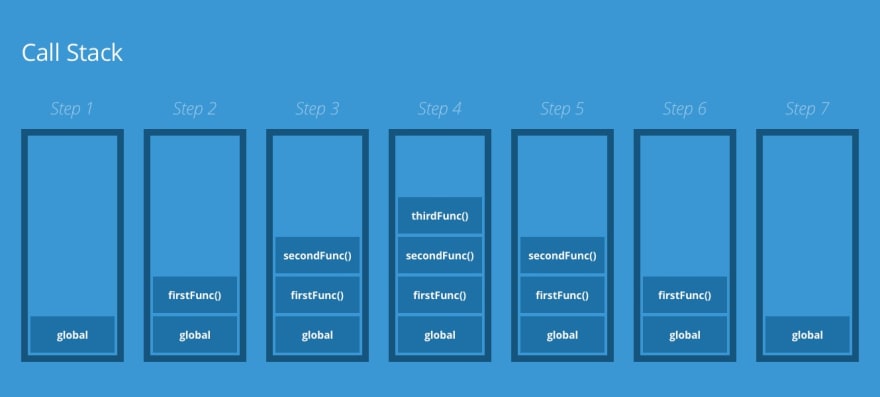
Example,
function thirdFunc() {
console.log("Greetings from thirdFunc()");
}
function secondFunc() {
thirdFunc();
console.log("Greetings from secondFunc()");
}
function firstFunc() {
secondFunc();
console.log("Greetings from firstFunc()");
}
firstFunc();
// Greetings from thirdFunc()
// Greetings from secondFunc()
// Greetings from firstFunc()
The Event Loop and The callback queue
解決的物題:讓 JS 可以執行非同步的動作(ex, network request)
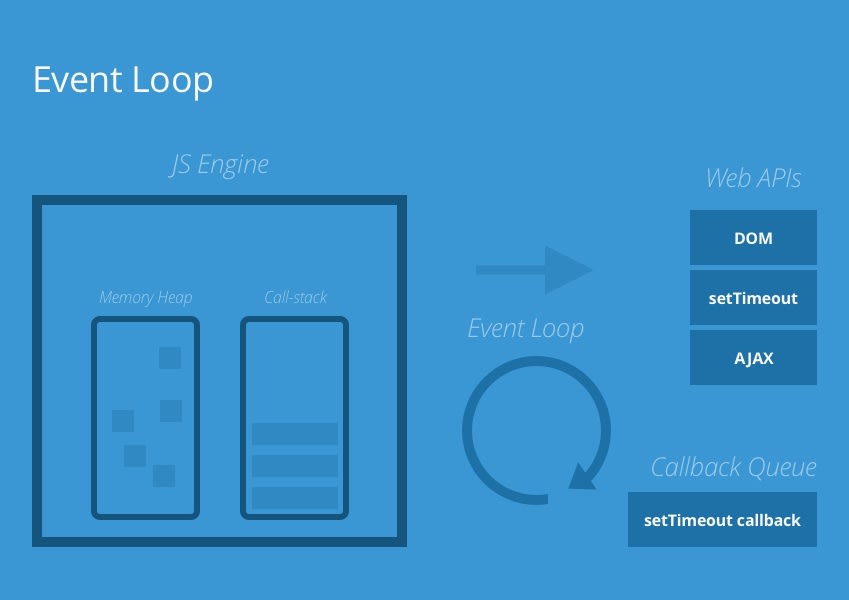
實際情況:The event loop追蹤 call-stack中需要執行 asynchronous 的 function,當執行到該 function 時把他丟入callback queue中(First-in, First-out),
- 當
call-stack其他 function 都執行完,變回空的時候。 - 處理
callback queue中的 function 丟回到call-stack上來執行。
callback queue的執行順序為: Microtask > Macrotask
常見的 microTask: Promise
常見的 macroTask: setTimeout, setInterval... (與瀏覽器或電腦底層的運作較有關係)
setTimeout(() => alert("timeout"));
Promise.resolve().then(() => alert("promise"));
alert("global ex. context");
// global ex. context
// promise
// timeout
補充:常見 eventLoop 順序判斷
注意:
- Promise 的 executor((resolve, reject) =>) 裡面的執行是同步
- then 會傳回一個 Promise 物件
- Promise 中的 executor 沒有 resolve 的話,結果會是 pending,且不會進行到下一個 then 中
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("1");
}, 0);
async function async1() {
console.log("2");
const data = await async2();
console.log("3");
return data;
}
async function async2() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log("4");
resolve("async2的结果");
}).then((data) => {
console.log("5");
return data;
});
}
async1().then((data) => {
console.log("6");
console.log(data);
});
new Promise(function (resolve) {
console.log("7");
// resolve()
}).then(function () {
console.log("8");
});
Resources
https://dev.to/thebabscraig/the-javascript-execution-context-call-stack-event-loop-1if1 https://pjchender.dev/javascript/note-event-loop-microtask/ https://juejin.cn/post/7004638318843412493#heading-10 https://juejin.cn/post/7016298598883131423